US vs EU vs UN Sanctions: What's the Difference? Visual Guide Inside
⚖️ I. Introduction - Why should foreign trade companies understand the differences in sanctions?
International trade in construction machinery has become increasingly complicated. With regulations tightening worldwide, sanctions play a more direct role in influencing exports of second-hand machinery than ever before. Sanctions can also interrupt or block a transaction at the level of payments, logistics, customer background checks, or compliance reviews.
Understanding the differences in U.S., EU, and UN sanctions is crucial for exporters and overseas buyers of secondhand excavators, loaders, cranes, and other construction machines. By knowing which rules apply and how they may affect your business, you can reduce risks, prevent costly delays, and protect the long-term stability of your cross-border business relationships.

🌐 II. Overview - Who designed these three sanction systems and how do they work?
US Sanctions
U.S. sanctions are most often issued under and administered by the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC).
A distinctive element of U.S. law is its long arm jurisdiction. Any transaction involving:
- U.S. dollars
- U.S. financial institutions
- U.S. firms
- U.S.-origin equipment, software, or technology
may fall under OFAC's scope.
Common categories of U.S. sanctions include:
- Comprehensive country sanctions
- SDN List: Specially Designated Nationals
- Sectoral sanctions
- Secondary sanctions targeting third-country companies assisting sanctioned entities
EU Sanctions
EU sanctions are collectively adopted by the European Council. They tend to:
- Focus on diplomatic, political, and human rights goals
- Apply uniformly across all the EU member states.
- Be less aggressive towards companies outside the EU compared to U.S. sanctions
UN Sanctions
The source of UN sanctions is UN Security Council resolutions.
These are to be implemented by each member state through its national laws.
UN sanctions often aim at:
- Global security
- Weapons control
- Conflict-affected areas
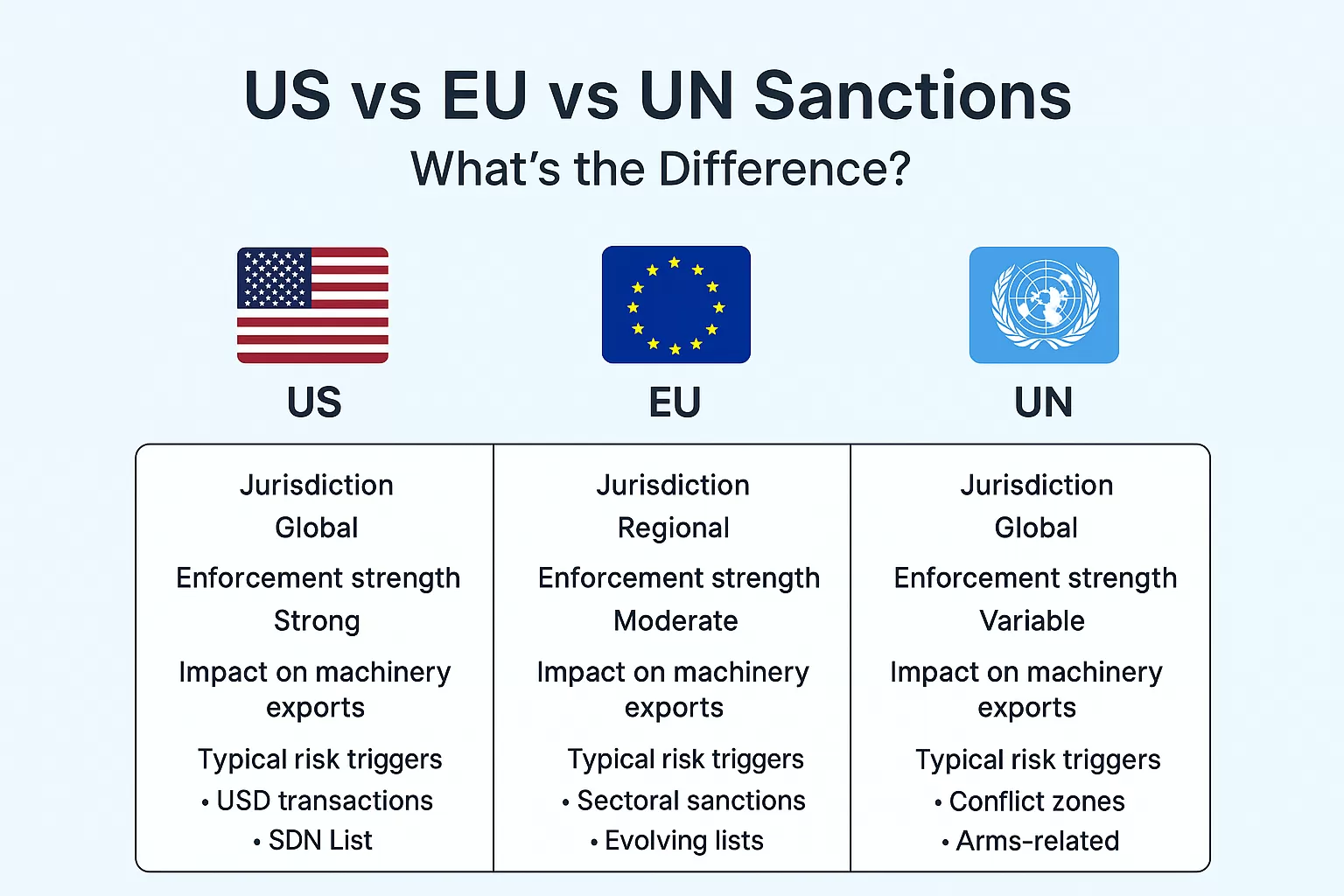
Compared to U.S. sanctions, UN measures generally have broader political intent but varying enforcement strength.
📊 III. Key Differences - Core Differences Between U.S., EU, and UN Sanctions
Various Responsible Authorities
- U.S.: OFAC
- EU: European Council
- UN: UN Security Council + Member State Enforcement
Different Enforcement Strength (U.S. Is the Strongest)
The US system is widely regarded as the most aggressive and comprehensive because of secondary sanctions and USD control.
Different Scope of Impact
- U.S. → Global influence via dollar-based transactions
- EU → Primarily regional but still impactful
- UN → Depends on implementation by each member country
Different levels of control over third-country companies
U.S. secondary sanctions can penalize companies even when neither party is American, if the activity supports a sanctioned target.
🏗️ IV. How Sanctions Affect the Second-Hand Construction Machinery Export Industry
1. Payment Compliance Risks
Banks are increasingly performing strict screenings of all international transfers; USD transactions may trigger OFAC checks. Payments originating from high-risk regions may undergo:
- Freezing
- Delays
- Rejections
This can interrupt machinery shipment schedules and cash flow.
2. Export Destination Restrictions
Some machinery, which may be in the domain of energy, mining, or infrastructure, could cause:
- Sectoral sanctions
- Export licensing requirements
- Additional compliance reviews for selected destinations
3. Obligatory Customer Background Checks (KYC)
Exporters shall ensure that:
- Company incorporation
- Directors and shareholders
- Ultimate beneficial owners (UBOs)
- Whether any party appears on the U.S., EU, or UN sanctions lists
This helps to avoid doing business with restricted entities.
4. Logistics and Customs Risks
Logistics providers may refuse high-risk routes. Customs authorities may:
- Hold shipments
- Request additional documentation
- Perform enhanced inspections
if they suspect possible sanctions violations.
📝 V. Practical Examples – Common Sanction Scenarios in the Machinery Industry
Examples include:
- Exporting concrete pumps, excavators, or loaders to restricted countries
- A buyer or beneficiary being listed on an SDN list
- Third-country transshipment patterns indicative of sanctions evasion
- Banks freeze cross-border payments for compliance investigation
📌 VI. Checklist of Compliance for Machinery Exporters
1. Customer Due Diligence (KYC & UBO)
Verify identities, ownership, and business activities.
2. Sanctions List Checking (US/EU/UN)
Use official lists such as OFAC SDN, EU restrictive measures, and the UN consolidated list.
3. Reviewing Payment Pathways
Avoid sensitive banks or financial intermediaries with past compliance issues.
4. Managing Intermediaries and Logistics Risks
Ensure freight forwarders and brokers comply with sanctions.
5. Sanctions Clauses in Contracts
This protects both sides in case sanctions change during the transaction.
📊 VII. Visual Guide – Comparison Chart of the Three Sanction Systems
🤝 VIII. How We Support You – How We Help Clients Manage Sanction Risks
As an experienced exporter of construction machinery, we support clients by offering:
- Professional compliance screening
- Mature banking and logistics networks
- Trade solutions for high-risk destinations
- Guidance on choosing the safest payment methods
- Transparent document management: invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, etc.
These measures help to guarantee safety, compliance, and efficiency in cross-border machinery transactions.
🔗https://zillionmachinery.com/🔍 IX. Conclusion - Understanding the differences in sanctions for safer cross-border trade
While the goals of U.S., EU, and UN sanctions are similar, the strength of their enforcement, scope of impact, and risks all vary. Proactive compliance, especially in the sphere of payments, customer screening, and logistics, is not an additional cost for exporters and overseas buyers. Rather, it is a long-term investment in secure business operation, stable partnerships, and smoother global trade.
FAQ
1. Why do sanctions affect second-hand construction machinery exports more directly?
Sanctions affect several parts of the export chain, including payments, logistics, customer background checks, and compliance reviews. Machinery shipment transactions involve cross-border bank transfers and multiple intermediaries with high-value transactions, triggering more frequent sanctions checks.
2. Are all construction machines restricted under U.S., EU, or UN sanctions?
No. Most standard construction machines are exported normally, such as excavators, loaders, forklifts, and cranes. Only equipment related to sensitive sectors would be put under additional screening or export controls, mainly energy, mining, infrastructure, or dual-use technologies.
3. Can a non-U.S. buyer or exporter be subject to U.S. sanctions?
Yes. Due to the system of the U.S. dollar and the long-arm jurisdiction of OFAC, even non-U.S. companies can be affected. If a transaction is in USD, involves U.S. banks, or touches U.S. technology, the deal may fall under U.S. compliance rules.
4. What happens if a buyer or logistics partner is on a sanctions list?
Banks can block the payments; customs can hold the shipments, and forwarding agents can decline to carry them at all. Exporters should immediately halt the transaction and conduct a review for compliance. Those who continue to ship despite sanctions risks will be heavily fined.
5. How can machinery exporters reduce the risk of sanction-related delays?
To this effect, exporters can minimize their risks through KYC/UBO checks, perusal of sanction lists (US/EU/UN), selection of safe banking routes, collaboration with only compliant logistics partners, and inclusion of relevant sanction-related clauses in the contract. Proactive compliance prevents shipment delays and payment issues.

 EN
EN en
en FR
FR nl
nl ka
ka ru
ru fa
fa ar
ar az
az pl
pl uk
uk hy
hy tr
tr mk
mk de
de pt
pt el
el es
es it
it sq
sq ky
ky